Das Bild zeigt eine Zusammenstellung verschiedener KarosserieBauteile von GF Casting Solutions für unterschiedliche Hersteller.
The future is big
In the past, vehicle bodies and structures were assembled from many separate pieces. In the future, the body and structure will consist of fewer and larger lightweight structural parts. This reduces weight and increases production efficiency, and it’s no different at GF Casting Solutions. Learn more in "Our Markets".
There is hardly another industry undergoing as many changes as the automotive industry, affecting vehicle electronics, in particular. For example, Volkswagen currently manages with 10 to 100 million lines of code in its cars’ software. It will likely soon be 200 to 300 million lines of code, according to the company and media reports.
What are the benefits of ‘big casting’?
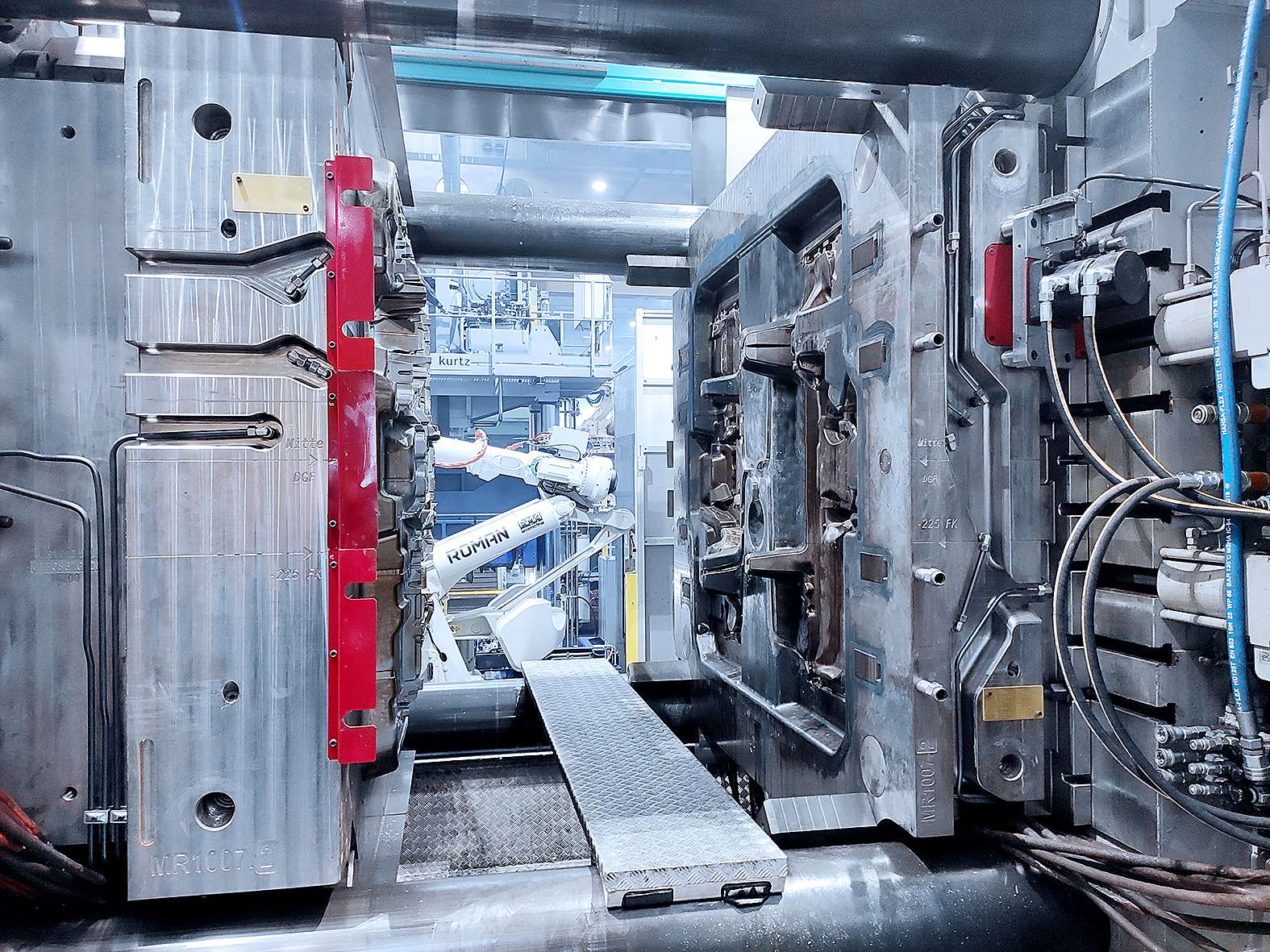
While IT systems and electronics are becoming increasingly multilayered, big casting in vehicle bodywork is reducing complexity on the customer side. Instead of many individual parts made of sheet metal or extrusion, die-casting machines produce, for example, a partial front end or a rear structure all at once. There are many advantages to reducing the number of separate pieces and work steps. Lower error rates and less waste save money and energy. The larger components are a precise fit and tailored to the respective vehicle model and customer requirements.
 © GF
© GFIn various development projects, GF Casting Solutions is working on integrating several separate pieces into one large component, which will in turn reduce the quantity of individual tools required and the complexity of jointing technologies, such as welding. “We have a big die-casting tool and on it the component is produced in only one shot. We are consistently implementing big casting in line with the GF Strategy 2025. We develop the components so that they can be produced on large die-casting machines with 4’400 tons whenever possible,” says Frank Gensty, Chief Technology Officer at GF Casting Solutions. This leads to significantly optimized jointing processes when it comes to connecting parts and assembly steps at the customer’s site.
Production time halved
Another advantage of big casting is time savings. “ Vehicle manufacturers can greatly reduce the production time of a vehicle when they assemble a complete front or rear end,” says Frank. As a result, a typical mid-size vehicle is produced in just 10 hours instead of 25. The production of larger parts and their installation also require corresponding adjustments to the plant technology on the customer side. According to Frank, many customers have already set a maximum number of the die-casting machines to be used in order to achieve the greatest possible efficiency with existing plant technology. At the same time, this also means that there need to be adjustments in logistics to accommodate the transportation and warehousing of larger parts, for example. The machines that produce the big castings are also naturally getting bigger and heavier. This in turn has a direct influence on the infrastructure of a plant.
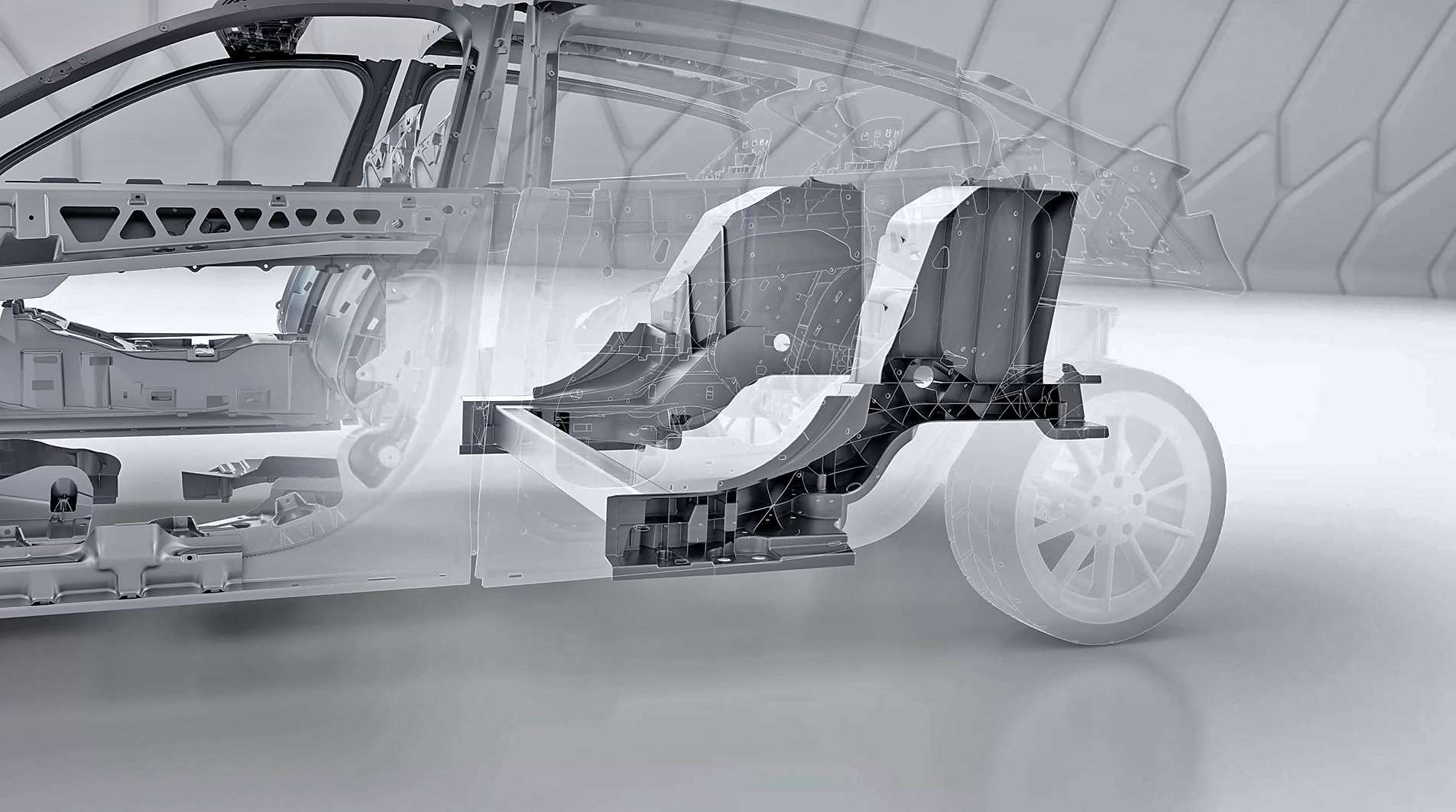 © GF
© GFSustainability is in the driver’s seat
GF Casting Solutions is developing a CO2 calculator for greater sustainability. This is an attempt to provide accurate information regarding the sustainability of production. According to Frank, “Every one of our customers will receive an explicit statement about the CO2 footprint of the cast component produced at GF. The advantage is that we can also use it to correctly simulate components in the development phase.” GF is already actively shaping the big casting trend, even though it is still in its infancy in the automotive industry. “We are in the middle of implementing it and developing the ideal solution for our customers in each individual case, combining lightweight construction, integration of features, performance, economic efficiency and ecological aspects,” continues Frank. According to the Chief Technology Officer, three major vehicle manufacturers in Europe are implementing big casting. “There are some companies that have not yet finalized the finer points of their strategy. What’s more, traditional vehicle manufacturers will push a 4’400-ton machine to its technological limits,” is how Frank analyzes the current situation in the growing market.
Klein, kompakt, leistungsstark
Lithium-Ionen-Batterien haben im Vergleich zu anderen Technologien die höchste Energiedichte: Sie können pro Kilogramm Batterie am meisten Energie speichern. Das macht sie zum Spitzenreiter für den Einsatz im E-Auto.
GF operates six die-casting sites, divided evenly between Europe and Asia, to ensure that production can always be as local as possible. This year, GF has also signed an agreement with the Bocar Group, a foundry that is headquartered in Mexico and specializes in lightweight components, to serve the US market. “We never stop trying to improve. Growth through innovation is a part of our DNA at GF,” says Frank with conviction.
What does ‘big casting’ mean anyway?
Big casting is a term used to describe the production of particularly large structural castings for vehicle bodies.

 © GF
© GFSpecial castings for electric cars
Electric cars need different components for the powertrain than vehicles with internal combustion engines. In terms of die-casting, these include battery housings and electric motor housings. Lightweight structural parts made of magnesium and aluminum lower the car’s overall weight.


